Manchester, historically known as an industrial hub with significant air pollution and environmental challenges, has long grappled with its industrial legacy. In 2023, Clean Cities rated Manchester as one of the worst European cities for clean and green transport infrastructure. Alongside Manchester, cities like Birmingham, Edinburgh, Glasgow, and even London were listed as lagging behind in sustainable transport development. But what steps has Manchester’s city council taken to make its transport infrastructure more sustainable in the 21st century? Next on manchestername.com.
Development of Green Transport Infrastructure
With the global conversation about climate change gaining momentum, municipalities worldwide have been adopting sustainable development measures to reduce their environmental impact. Manchester is no exception. Since the early 21st century, the city has been transforming its transport infrastructure to pave the way for a greener and more sustainable future. From cutting-edge electric tram networks to innovative bike-sharing schemes, Manchester aims to become a leader in mobility and carbon emission reduction.
Modern Transport Infrastructure in Manchester
One of Manchester’s first “green” public transport initiatives was the Metrolink, a modern light rail transit system connecting the city and its suburbs. Serving thousands of passengers daily, Metrolink provides a fast, efficient, and environmentally friendly mode of transport for residents and visitors alike.
Complementing the Metrolink is Manchester’s growing network of cycling infrastructure. This includes bike lanes, bicycle rentals, and incentives to encourage cycling. The city launched its first bike-sharing scheme in late 2021, promoting cycling as a practical and eco-friendly way to navigate the city. By opting for bicycles, Manchester residents reduce traffic congestion and improve air quality.
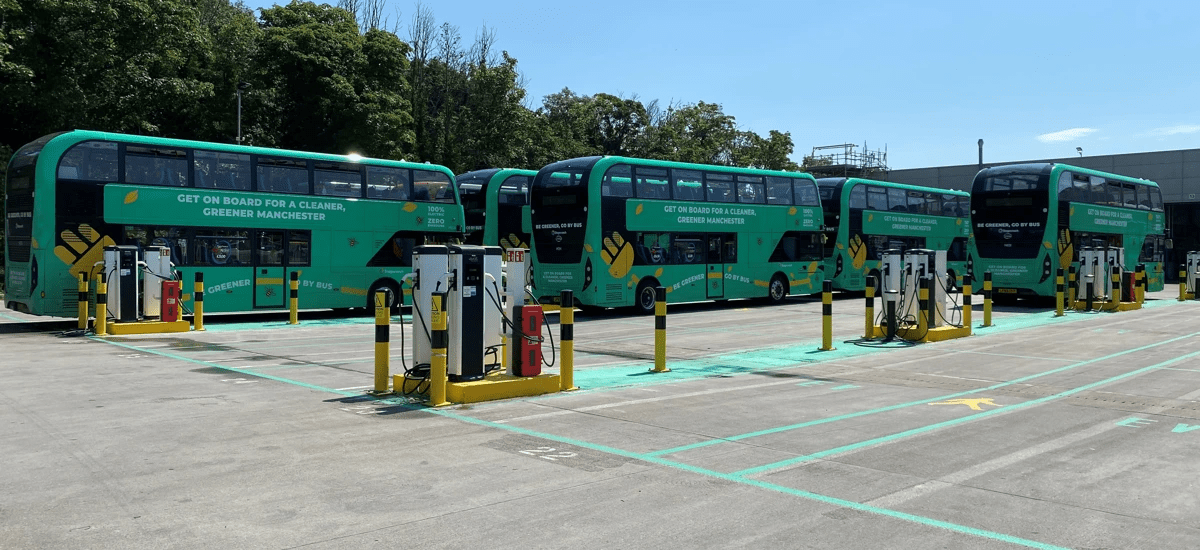
Manchester also boasts a fleet of free public electric buses. These buses operate on three routes, connecting major railway stations, hotels, shopping centres, and business districts. This service enhances accessibility while minimising emissions.
Manchester has also embraced smart mobility technologies, optimising transport systems and improving travel experiences. Real-time traffic monitoring, ticketing systems, and fare integration are part of the city’s strategy to modernise transport infrastructure.
Walking remains one of the most sustainable modes of transportation, and Manchester has invested in pedestrian infrastructure to make walking a comfortable and attractive option. Key landmarks, historical sites, and shopping centres are all within walking distance in the city centre, making it convenient for environmentally conscious residents and tourists to explore the city on foot.
Criticism of Manchester’s Transport Infrastructure
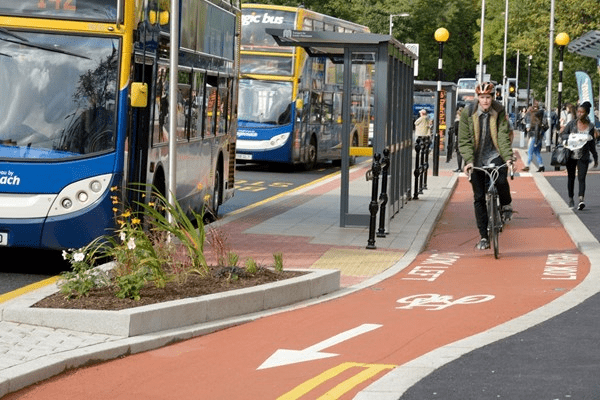

Despite its efforts, Manchester received harsh criticism in 2023 from Clean Cities for its shortcomings in sustainable transport infrastructure. The report highlighted the city’s limited availability of eco-friendly public transport options. For instance, when Clean Cities representatives visited Manchester, they hoped to explore the city using bicycles. However, they found no bike rentals available at any nearby docking stations and had to rely on taxis instead. This incident, reported “The Guardian” underscored gaps in Manchester’s green transport initiatives.
While Manchester has eco-friendly transport options, these are concentrated in specific areas, leaving room for expansion and improvement.
The city council is actively working on plans to expand the Metrolink network and improve pedestrian infrastructure. Such developments will contribute to a healthier and more environmentally friendly urban environment.
Manchester’s journey toward sustainable transport reflects its commitment to addressing its industrial legacy while striving for innovation and resilience. With continuous improvements, the city aims to bridge the gap between criticism and progress, ensuring a greener future for its residents and visitors.
